As the volume of content output increases, it’s becoming more difficult to capture attention, which also means that the value of attention is increasing.
So if you have excellent SEO and content marketing skills and understand how to capture an audience by driving traffic from Google (and other search engines), there are plenty of different ways you can make money.
Most people know you can sell SEO services, but that isn’t the only way to make money online.
In this post, we’ll discuss different ways to make money with SEO online, the pros and cons of each monetization strategy, and some specific examples to inspire you.
1. Sell SEO Consulting and Freelance Services
Plenty of businesses are willing to pay SEO professionals to help them do an SEO competitor analysis and rank for keywords that their target audience searches.
Whether it’s a local business selling flowers or a tech company selling data management software, ranking for keywords that potential customers search on Google (e.g., “best flower delivery in Austin, TX” or “best data management solutions”) is incredibly valuable.
You can operate as a solo SEO consultant or freelancer and do the work yourself, or you can build an agency and hire others to execute your SEO process.
Some services that you might offer include SEO audits, link building, content marketing, on-page optimization, and technical SEO. If you’re starting your SEO career, pick one service and then add other services as you become more confident in your abilities.
It’s also a good idea to niche down and specialize in a particular industry (SaaS, local businesses, ecommerce, etc.) as businesses are often willing to pay more for a specialist.
You can also do SEO for podcasting, YouTube, and Amazon, as ranking at the top of those search engines is also extremely valuable.
Want us to
scale your traffic?
For the first time, The Copyblogger methodology is now available to a select few clients. We know it works. We’ve been doing it since 2006.
Examples of SEO Consultants/Agencies
Brodie Clark is a solo SEO consultant who has built a name for himself in the search engine optimization community. If you’re interested in going down the solo consultant or freelancing route, consider building a following on social media or a newsletter, as these channels help him generate clients.
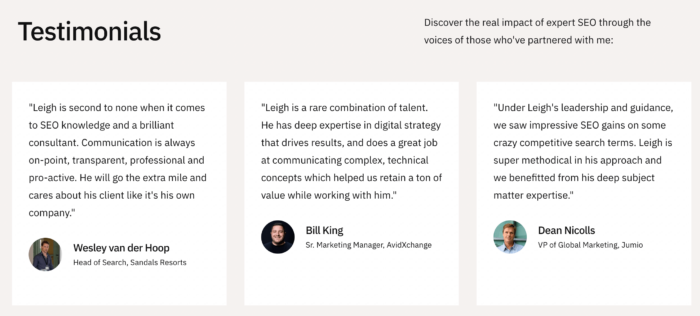
Leigh McKenzie is another example of an SEO consultant. He displays a number of testimonials on his site from satisfied clients, which support the strategic SEO solutions he offers.
If you create an agency, the key to success is establishing repeatable systems and processes that make it easy for any employee to implement and generate the same results for all your clients.
Digital Commerce Partners is the SEO and content marketing services division of Copyblogger.
The agency’s site highlights their data-driven processes that increase organic traffic and conversions.
Pros of This Model
- Immediate cash flow and few startup expenses.
- High profit margins.
- Learn on other people’s websites.
Cons of This Model
- Clients can churn at any time (and this happens as SEO takes time to drive results).
- Some people don’t enjoy client management.
- Limited scalability as solo consultants can only raise their prices to scale, and agencies require more people to scale.
Earning Potential
SEO services range dramatically. Some companies will pay their SEO agency $30,000 plus per month, whereas others may pay a consultant a few thousand dollars per month for SEO services.
The price you charge depends on the ROI you can produce for the company. For example, if you drive 20 customers worth $40 per month for a florist, you’ll make significantly less money than if you can drive 10 new customers worth $2,000 each for an enterprise tech company. Your expertise and skill level will also impact how much you can charge.
However, here are some stats from Ahrefs:
- Average SEO retainers range from $500 to $1,500 per month.
- Most SEO consultants charge $75 to $100 per hour.
2. Sell Productized SEO
If you want to work with clients but don’t like the idea of long-term engagements, you can productize your SEO services.
For example, you can offer an SEO strategy package that includes a technical audit, keyword research, a content marketing strategy, and a link-building strategy. Then, you give this data to the client, and they are responsible for the execution.
So unlike SEO services, these engagements might take you a week or two to complete, and then you part ways with that client.
Examples of Productized SEO
Marie Haynes offers productized SEO projects. Specifically, she analyzes declines in organic performance, your competitor landscape, and a future strategy map. This engagement costs $6,500 with a call and $5,000 without a call.
You can view the details of her productized services on her website.
Pros of This Model
- Less client management than providing services.
- Immediate cash flow and no overhead to get started.
- You aren’t responsible for a drop in rankings or other problems that crop up with the website.
- Often 100% profit margins.
Cons of This Model
- You don’t have any recurring revenue, so you’re always selling.
- Many bigger companies with bigger budgets are only interested in hiring someone who can execute for them.
Earning Potential
According to Ahrefs’s statistics, these projects usually cost between $2,501 to $5,000. It’s also a nearly 100% profit margin business model as the only expenses you’ll have include SEO tools (like Semrush or Ahrefs) and any basic operational costs, like billing management.
3. Create An Affiliate Website
If you have a website with an audience, you can partner with other businesses that want to sell their products and services to your audience.
These businesses give you a link, and anytime someone from your website clicks on that link and purchases the product, you receive a sale commission.
This business model is called affiliate marketing, and it’s an easy way for you to make money selling products and services to your audience without handling customer success or fulfillment. In fact, it’s like influencer marketing, though all of your revenue is based on commission, and you also don’t have to have a personal brand behind the website.
You’ve probably already seen plenty of affiliate sites.
For example, the Spruce is an affiliate website, and if you were to purchase one of these air fryers through the link on the Spruce website, they would receive a commission:
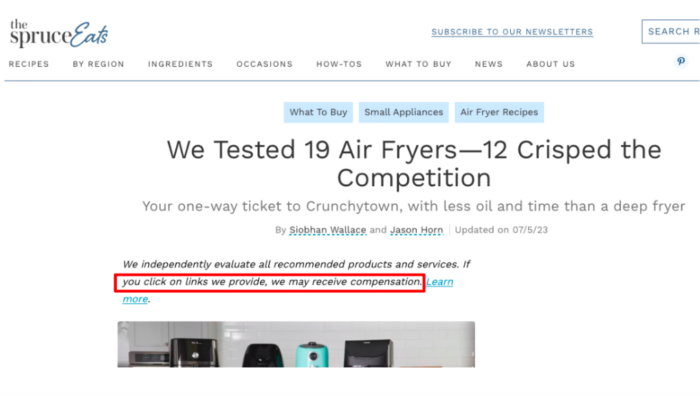
While The Spruce is an example of a massive affiliate website, most independent SEOs create small affiliate websites in different niches, like pets, gardening, tech, etc.
In fact, many SEOs create a portfolio of different websites in various niches.
Examples of Affiliate Websites
Wirecutter is an example of an affiliate website. Essentially affiliate websites build organic traffic and then monetize them by creating pages for “best (product)” keywords and listing their affiliate products.
Ahrefs has a great video of various affiliate websites:
Pros of This Model
- You don’t have to talk to any of the clients and can make passive income.
- There is no limit to scaling an affiliate website, and you can build it into a substantial brand.
- You can be a solo operator and never have to hire an employee.
Cons of This Model
- Building a loyal audience can take a long time, so you won’t see immediate cash flow.
- Google’s algorithm can change at any moment and drastically change your income.
- As AI content takes over and EEAT becomes more important, Google is cracking down on affiliate websites.
Earning Potential
The earning potential of an affiliate website varies depending on the niche you invest in, how much content you produce, and the value of the audience (i.e., an auto insurance audience is more valuable than an audience of baking enthusiasts).
Statistics show that about 42% of affiliate marketers make more than $10,000 annually, while the other 58% make less than $10,000 annually.
However, there are also plenty of affiliate businesses that generate multiple millions of dollars annually.
4. Offer Sponsored Content
Many branded and personal bloggers monetize their audiences by allowing other brands to create and publish sponsored posts on their websites.
Here’s an example of a sponsored blog post from a branded blog:
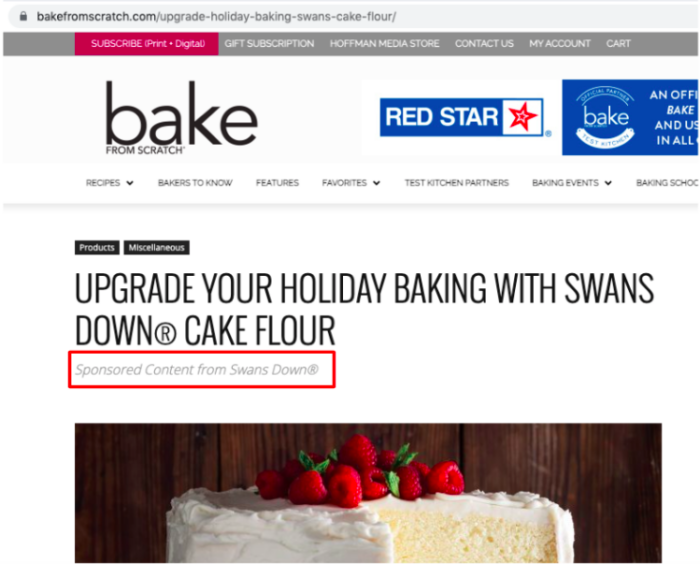
Many brands will also be happy to pay for guest posts if you allow them to insert a link to their website as backlinks are valuable for improving domain authority.
Examples of Websites With Sponsored Content
An example of a brand that offers sponsored content is the Mom Collective. You can see that they offer sponsored blog posts, among other promotional services.
Here’s an example of one of their sponsored blog posts:
There are also plenty of personal bloggers that offer sponsored content. Here’s an interesting income report from Get On My Plate, a food blogger. She offers sponsored posts as well as various other income streams.
Pros of This Model
- You don’t have any client management challenges.
- You can increase your prices and scale your income as your website grows.
- Publishing sponsored posts written by other people requires very little effort.
Cons of This Model
- There isn’t any recurring revenue, and you’re always trying to sell new sponsors.
- As audiences gravitate more towards social media for information, individual passion blogs are generating less traffic.
- To keep trust with your audience, you’ll need to keep a balanced ratio of helpful to sponsored content (probably 4:1), which can limit scale.
Earning Potential
Statistics from AdWeek show that the average sponsored post is about $300. However,you can charge more depending on your traffic volume, audience loyalty/engagement, and website authority.
5. Rank and Rent Pages
While some business owners pay for SEO services to optimize their websites, others simply want immediate leads. So if you can create a website that ranks for a keyword the business wants to rank for, they’ll often simply pay you to rent that ranking website to generate leads.
For example, a dentist in Austin, TX, might pay to rank your website if you currently rank first for “best dentist in Austin, TX.”
Matt Diggity has an excellent guide to creating rank and rent websites:
Examples of Rank and Rent Websites
Grand Rapids Tree Care is an example of a rank and rent website. The owner reported that it makes about $2,000 per month:
You can see various other examples of rank and rent websites on this page.
Pros of This Model
- High profit margins.
- Minimal client management.
- You have complete control over the SEO strategy.
Cons of This Model
- You’ll lose your business if your website isn’t ranking well.
- It requires a lot of upfront investment to get websites to rank.
- Clients may churn at any time.
Earning Potential
Most rank and rent websites make a few thousand dollars per month, though your profit depends largely on the niche you select (the value of your leads) and how well your website ranks.
6. Grow and Flip Websites
As SEO is a long game, and it can take years for a website to rank for its desired keywords, many businesses prefer to purchase existing websites with quality content, backlinks, and a decent amount of traffic for their target keywords.
Many of these buyers will then create and sell their own products on these websites or redirect your website to one of their existing websites to increase its traffic and authority.
The key to growing and flipping a website is building a solid foundation with room for more growth and monetization. To ensure your website is flippable, here are a few tips:
- Use a branded domain name
- Select a niche with room for expansion and growth
- Use primarily white hat growth strategies to show steady growth
When you’re ready to sell your website, you can use a marketplace like Quiet Light Brokerage, Flippa, or FEInternational to list and sell your website.
Jase Rodely has a great guide to flipping websites.
Examples of Website Flipping
If you want to find examples of website flipping, check out Flippa, as you can see websites for sale and various metrics like asking price, traffic, backlinks, and niches to estimate how much you can sell a website for depending on its authority and organic search traffic.
Here are just two current examples:
Pros of This Model
- It’s one of the more profitable SEO models, as you can generate a 20-30x return on net income profits.
- It doesn’t require any client management.
- It can generate passive income while you grow it and then a lump sum of cash when you sell it.
Cons of This Model
- It requires a lot of upfront investment to generate the initial website traffic.
- The acquisition process can be time-consuming, nerve-wracking, and complex.
- There is no guarantee that anyone will acquire your website.
Earning Potential
SEO expert Matt Diggity estimates that the average website can sell for about 20-30x its net income profit, so your income potential depends largely on the profitability of the business you build.
7. Create a Dropshipping Website
An easy way to monetize your traffic is by selling physical products. However, if you want to avoid dealing with the headache of manufacturing and shipping products, you can partner with a manufacturer to handle the logistics. Then, all you have to do is advertise and sell their products on your website.
This business model is called dropshipping, and it’s essentially an ecommerce store that doesn’t require you to do any of the fulfillment yourself.
You could also build a dropshipping business through Amazon and then do Amazon SEO to rank and sell your products, though many SEOs prefer to create and rank their own stores on Google, as Amazon can copy your products.
The SEO work involved with an ecommerce website tends to involve product page and website architecture optimization, so it’s a great option for technical SEOs.
Dropship Breakthru has an excellent dropshipping guide with more details on how you can start your own dropshipping business.
Examples of Dropshipping Websites
This cuckoo clock shop is likely a dropshipping website. They partner with various cuckoo clock manufacturers, and then when people place an order on their website, they send the order to the manufacturer, who then sends the clock to the customer. The dropshipper’s profit is the difference between the retail price the customer pays and the wholesale price the manufacturer charges plus other operational and marketing expenses.
Another example of a more established dropshipping website is Texas Snax. Today, it’s a $3 million dollar dropshipping business that sells Buc-ee’s merchandise online.
You can read the full story here:
Alternatively, if you’re interested in just growing a dropshipping website to sell it, you can read this case study about a dropshipper that sold their website for $130,000.
Pros of This Model
- You can monetize the website by selling physical products without actually handling any of the fulfillment yourself.
- You can scale your profitability by adding more products and expanding into parallel niches.
- These businesses are also sellable, so you can flip them for a significant profit.
- You can run a dropshipping business as a solo entrepreneur.
Cons of This Model
- You don’t have much control over product quality or customer service, which can damage your brand’s reputation.
- You will probably compete with other dropshippers selling from the same manufacturer.
- You’ll have to deal with customer complaints yourself, which can be a headache.
- It can take a long time to see an ROI, as you’ll still need to build the website and generate traffic before generating any profit.
- If your product rankings drop and you can’t drive traffic to your product pages, your business will disappear.
Earning Potential
The earning potential of your store depends on your profit margins and the number of products you sell. In addition to the wholesale prices, some factors to consider when determining profit margins include shipping costs (if you offer free shipping), customer support (if you hire someone else to help you with this), and product returns.
Statistics show that the average profit margin for a dropshipper is 20-30%, and the average dropshipping store usually makes about $1,000-$5,000 per month.
8. Sell Your Own Digital Products
While dropshipping is one way to monetize your website by selling a manufacturer’s physical products, another popular method is creating and selling digital products.
A digital product could be an app, a course, or a community, and the benefit of selling digital products is that you create it once and sell it infinitely. This makes it an excellent, scalable passive income business.
If you intend to sell courses or educational content, you’ll need to rank for your desired keywords and ensure the content builds trust with your audience. People want to learn from experts, so you may also want to build a personal brand around your website.
Examples of The Digital Product Model
The Copyblogger Academy is actually an excellent example of this business model.
It’s a community for writers in the creator economy, and most of our members originally found the community through the Copyblogger website. Our main growth strategy here at Copyblogger is writing helpful SEO content, so you can use the same blueprint to build an audience through SEO and then monetize that audience through a digital product.
Marie Haynes is also an excellent example of a creator who has leveraged her SEO knowledge to build digital products, like her $150 Helpful Content Workbook.
Pros of This Model
- Digital products scale well because you can build once and sell infinitely.
- Digital products also require minimal customer support (unless you have a community).
- You can offer upsells, downsells, and subscriptions to increase the lifetime value of your customers.
- Most digital products require minimal upfront investment to create.
Cons of This Model
- You typically need to establish a higher level of trust to sell an educational-based product because people want to buy from experts. Therefore, your content must not only rank well but also build trust, which can increase your content production costs.
- It takes time and resources to build deep trust with an audience, and you may have to nurture them through email and free trainings before they’ll consider purchasing your digital products.
Earning Potential
One of the key benefits of this model is that the earning potential is essentially limitless. The average price point is usually around $1,000 if you’re selling a course, so your revenue will depend largely on product demand (market size) and how much your audience trusts your brand.
However, you can also sell ebooks, downloadable templates, and other products for a few hundred dollars.
9. Get a Job As An SEO Specialist
Most established companies hire full-time SEO specialists to help their brands rank for critical keywords. In addition, the introduction of AI will likely change the SEO landscape, and people who know how to automate various SEO processes with AI will be increasingly valuable to companies.
There are also plenty of remote and in-person jobs at various companies, so you can enjoy a stable salary and still travel the world as an SEO professional.
You can also learn on the job and then build your own websites to add additional income streams.
Examples of SEO Jobs
You can get a job as a general SEO specialist or various subsets of SEO, like link building, content writing, or technical SEO.
Just search on Indeed or LinkedIn to find hundreds of different SEO jobs:
Some examples of successful SEO experts that began as in-house specialists include Alexandra Tachalova (previously at SEMrush) and Kevin Indig (previously at Shopify).
Pros of This Model
- You receive a steady income that isn’t dependent on Google’s algorithm.
- You can learn SEO on someone else’s dime and then create secondary income streams by building your own websites.
- You can leverage another brand’s authority to build your own personal brand in SEO by receiving speaking opportunities and other event invitations.
Cons of This Model
- You still work for someone else, so you don’t have as much freedom as other SEO monetization strategies.
- You have limited experimentation opportunities as you must respect the company’s other goals.
- It has limited earning potential.
Earning Potential
The average SEO salary is about $56,000 according to Glassdoor, but a senior SEO manager can make a healthy six figure salary.
How To Take Action Now
The best way to become great at SEO is by practicing SEO.
So the best advice I can give you is to set up your own WordPress site and start writing content to rank for various keywords.
While you might not make money immediately, it’s the fastest way to improve your SEO skills. As you become a better SEO professional, you’ll have more opportunities to monetize that skill, from selling services to clients to building passive, cash-flowing affiliate sites.
If you want more help getting started as an SEO professional, consider joining the Copyblogger Academy. It’s a group of like-minded creators leveraging SEO to fuel their businesses. You’ll also receive direct access to me, and I host regular interview sessions with other top performers in the creator economy.
You can check it out today risk-free, as I offer a 30-day money-back guarantee.

This article's comments are closed.